The publication defines zero trust (ZT) as a collection of concepts and ideas designed to reduce the uncertainty in enforcing accurate, per-request access decisions in information systems and services in the face of a network viewed as compromised. A zero trust architecture (ZTA) is an enterprise’s cyber security plan that utilizes zero trust. Trust Network Provides an online discussion forum for ABA member corporate fiduciaries and wealth management professionals. This site is a private meeting place that provides members of ABA Trust Network with a shared calendar, discussion forums, member profiles, file storage and more. Over a series of three blogs (of which this is the first), we will take a deeper dive into the aspects of the Networking pillar in the Microsoft Zero Trust security model. We will go through each of the dimensions listed (network segmentation, threat protection, and encryption) and show design patterns and helpful guidance on using Microsoft Azure services to achieve optimali.
As countries around the world work to overcome the COVID-19 pandemic and restart their economies, they all face the challenge of how to reopen their borders and allow travel and commerce to resume while protecting their populations’ health. As they contemplate relaxing border restrictions, quarantine and lock-downs, governments and industry need a more trustworthy model for validating individuals’ health status.
The Challenge
At present, COVID-19 test results are frequently presented on printed paper - or photos of the paper - from unknown labs, often written in languages foreign to those inspecting them. There is no standard format or certification system for lab results. Similarly, vaccination records are still generally shared on easily-forged paper cards.
The availability of trusted, verifiable health status information, including test results and vaccination records, can help governments implement more flexible, risk-based policies and develop a more reliable assessment of individuals’ health status as a part of a multi-layered risk management approach. Several countries have implemented digital platforms for travellers to submit their health information prior to departure. However, given the interconnectedness of global travel and the global economy, it is not practical for each country or jurisdiction to implement its own independent methods for verifying the health information of incoming travellers from every other country or region. Such an approach would impose an overwhelming burden of complexity on governments, industries and individuals alike.
Common Trust Network
To address this challenge, The Commons Project Foundation and the World Economic Forum have launched the Common Trust Network in collaboration with a broad voluntary network of public and private stakeholders to help ensure that only verifiable lab results and vaccination records from trusted sources are presented for the purposes of cross-border travel and commerce.
The Common Trust Network is designed to:
- Empower individuals with digital access to their health information so they can demonstrate their health status while protecting their data privacy.
- Provide governments a trustworthy model for verification and acceptance of foreign lab tests and vaccination records, whether digital or paper-based.
- Support airlines, airports, cruises, hotels, employers and venues to rely on a trusted health certificate without having to verify it themselves or hold any data.
- Enable a clearer understanding of health entry requirements for destinations for all stakeholders involved
The Common Trust Registry
The Common Trust Network is enabled by a global registry of trusted laboratory and vaccination data sources, standard formats for lab results and vaccination records, and standard tools to make those results and records digitally accessible. The Registry is operated on a not-for-profit basis as an open, shared service for the common good.
The Common Trust Network is also enabled by a common global registry for governments and other destinations to publish their health screening entry rules in a common format, making it easier for travellers and the travel industry to understand and comply with each destination’s requirements. The Registry is composed of:
● CommonTrust Data Sources. Participating health organizations, including labs and vaccination sites, agree to provide individuals with digital access to their health information using open, globally-interoperable standards (e.g. HL7 FHIR, W3C verifiable credentials). Data Sources agree to provide individuals with access to their information via one or more of the following:
- Apple Health (iOS) / CommonHealth (Android)
- Other digital wallet apps
- Paper printed with QR codes containing W3C verifiable credentials.
These Data Sources also agree to be listed as issuers on the CommonTrust Registry. Participating governments are invited to designate Data Sources in their jurisdictions as Approved Sources.
● CommonTrust Destination Rules. Participating countries, jurisdictions and other destinations (airlines, ships, public transport, hotels, venues, events, offices, schools...) agree to publish and maintain their health entry requirements using a standard machine-readable format in the CommonTrust Registry.
CommonTrust Network Principles
The Common Trust Network is vendor and technology agnostic and is guided by a commitment to the following core design principles:
Openness & Interoperability: based on international standards and open technologies and interoperable across countries and regions.
Transparency: operated in an open and transparent manner
Neutrality: operated as a common shared service for the benefit of all stakeholders
Sustainability: operated on a sustainable not-for-profit basis.
Privacy by Design: upholds and protects the privacy of individual health data and designed to comply with applicable data privacy regulations.
Flexibility: designed to adapt over time as the pandemic and science evolve.
Inclusivity: accessible and usable by all people and countries regardless of level of wealth and economic development.
The Forum supports the emerging ecosystem of solutions, providers, and travel/health passes all aiming to restore cross-border mobility. The two registries can be leveraged by any other stakeholders committed to openness, interoperability and global standards.
Author(s)
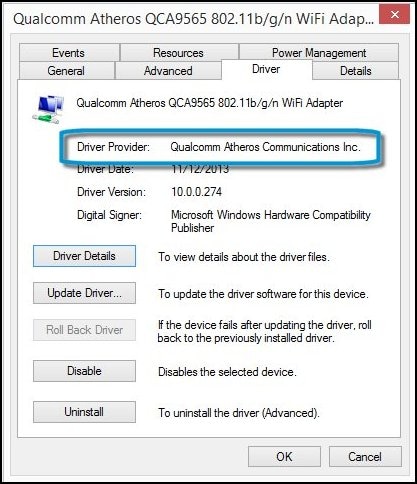
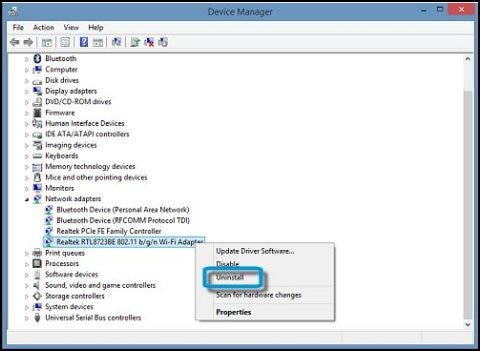
Trust Network & Wireless Cards Driver Download For Windows 10 Free
Abstract
Zero trust (ZT) is the term for an evolving set of cybersecurity paradigms that move defenses from static, network- based perimeters to focus on users, assets, and resources. A zero trust architecture (ZTA) uses zero trust principles to plan industrial and enterprise infrastructure and workflows. Zero trust assumes there is no implicit trust granted to assets or user accounts based solely on their physical or network location (i.e., local area networks versus the internet) or based on asset ownership (enterprise or personally owned). Authentication and authorization (both subject and device) are discrete functions performed before a session to an enterprise resource is established. Zero trust is a response to enterprise network trends that include remote users, bring your own device (BYOD), and cloud- based assets that are not located within an enterprise-owned network boundary. Zero trust focus on protecting resources (assets, services, workflows, network accounts, etc.), not network segments, as the network location is no longer seen as the prime component to the security posture of the resource. This document contains an abstract definition of zero trust architecture (ZTA) and gives general deployment models and use cases where zero trust could improve an enterprises overall information technology security posture.
Trust Network & Wireless Cards Driver Download For Windows 10 Download
Download Paper
Trust Network & Wireless Cards Driver Download For Windows 10 Full
Keywords
Trust Network & Wireless Cards Driver Download For Windows 10 64-bit
